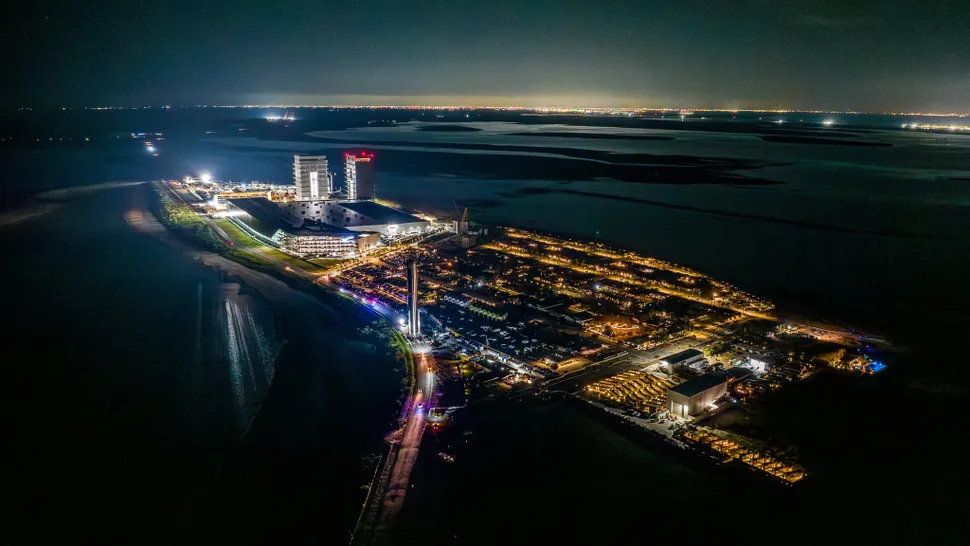

SpaceX has moved its giant Super Heavy booster to the launch pad for Starship Flight 10. Here’s what this means for the mission timeline, upgrades, and future launches
Super Heavy Booster Rolls Out to the Pad
The sight of SpaceX’s massive Super Heavy booster slowly rolling out to the launch pad is more than just another rocket move—it’s a signal that the world’s most powerful launch system is gearing up for its next big leap. At nearly 70 meters tall, the booster
also read SpaceX Starship 10th Test Flight Set After Explosive Setbacks
looks like a moving skyscraper as it is carefully transported on a giant carrier. Every rollout sparks excitement, because it represents the final stage before a full integrated test with the Starship upper stage. Engineers use this moment to check road clearances, ground
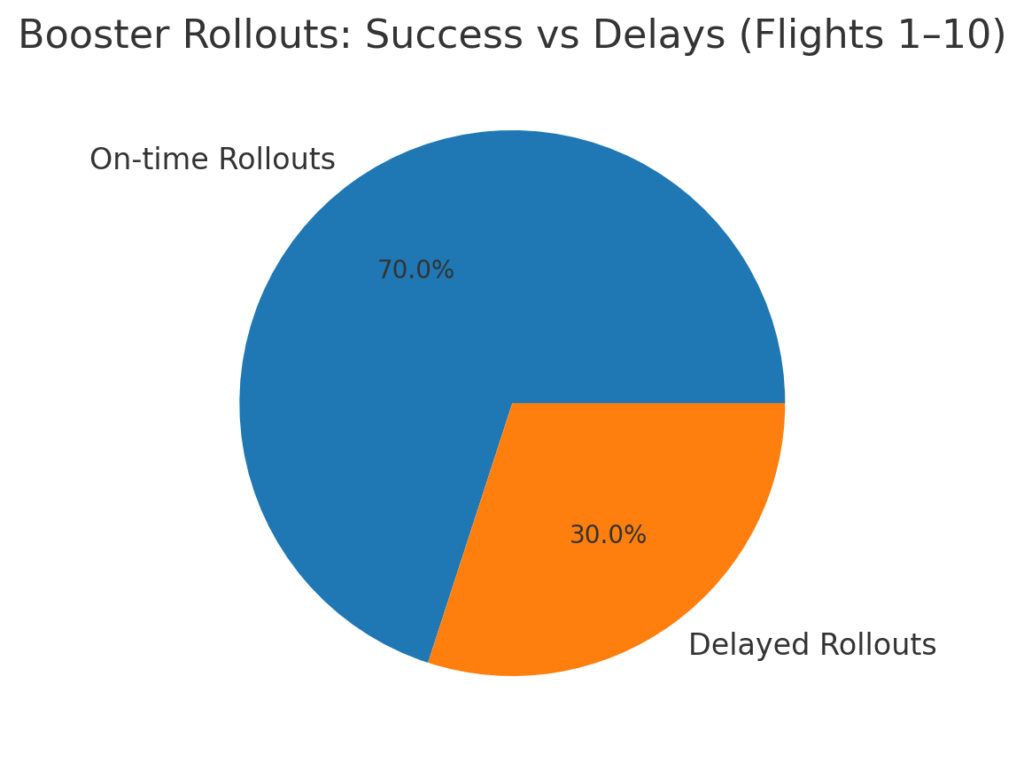
systems and the connection between pad structures and fueling lines. Rolling the booster out is not just logistics, it is a practice in precision and safety, where even a slight miscalculation can create delays. For the upcoming Flight 10, the super heavy booster rollout has gained
extra attention since previous test attempts ended in explosions. Fans and experts alike see this as a turning point—if the booster systems perform as expected
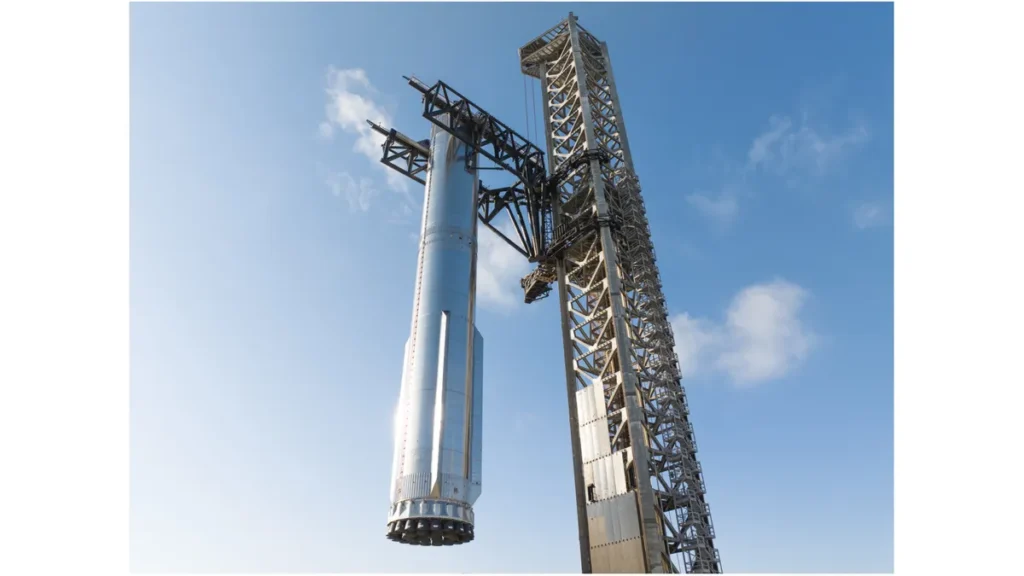

Starship could finally edge closer to proving its reliability. This single rollout is a visible reminder that each small step, no matter how slow, is part of SpaceX’s bigger dream of reaching Mars.
Why This Movement Signals a Major Step Forward
The rollout of the massive Super Heavy booster to the pad is more than just a logistical move—it’s a signal to the world that SpaceX is almost ready for its biggest test yet, the Starship Flight 10. The sight of the towering rocket moving across the Texas launch site grabs global attention because it represents years of engineering progress and thousands of hours
of work. Each rollout brings engineers a step closer to the launch campaign, where every nut, bolt, and weld must prove its strength. For the tenth test flight, SpaceX has added significant structural upgrades, making this rollout even more meaningful. In simple terms
also read SpaceX Falcon Heavy to Launch X-37B Space Plane for US Space Force Mission Today, the rocket is no longer an experiment—it’s on the path to becoming an operational launch vehicle. This step shows confidence that earlier problems are now better understood. From here, teams will connect propellant lines, run static fire tests, and double-check systems.
Once complete, the super heavy booster will be stacked with the Starship upper stage. The world now watches as this pad move sets the stage for one of the most ambitious launches in modern spaceflight history.
What’s New in This Version of Starship
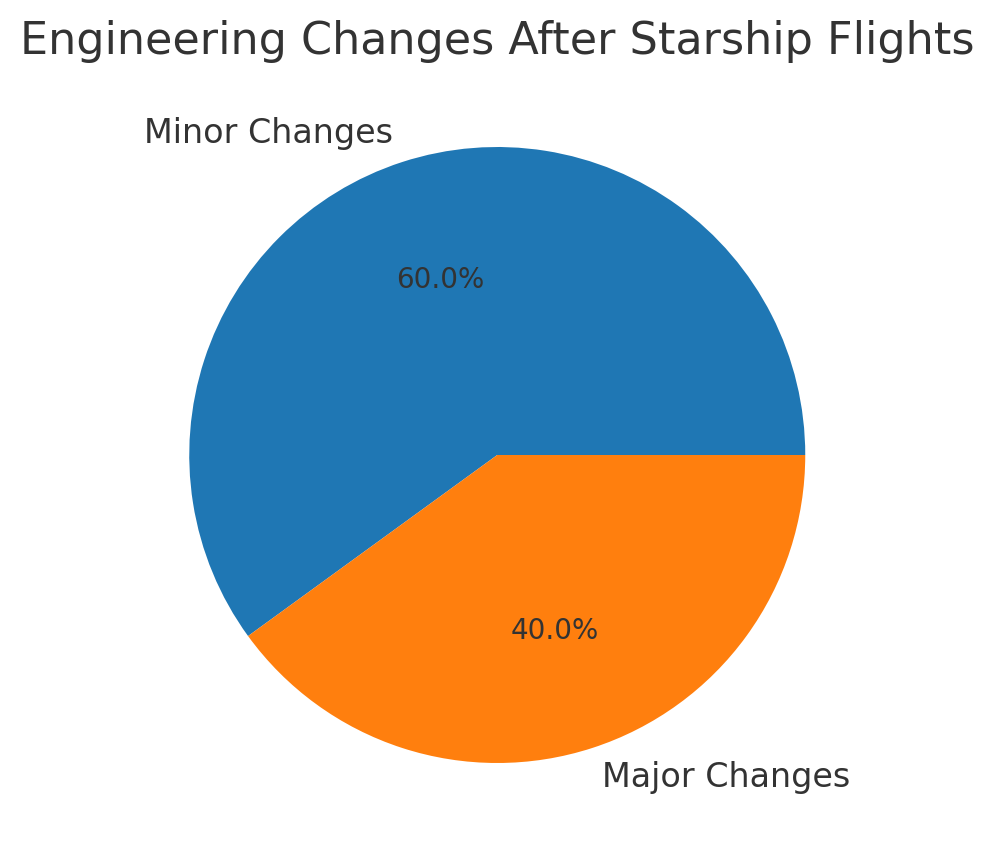
SpaceX doesn’t just repeat old designs—it evolves. Each Starship flight has introduced engineering changes, but Flight 10 stands out because it includes lessons learned from nine past flights. This version of Super Heavy carries upgraded heat shield tiles, reinforced
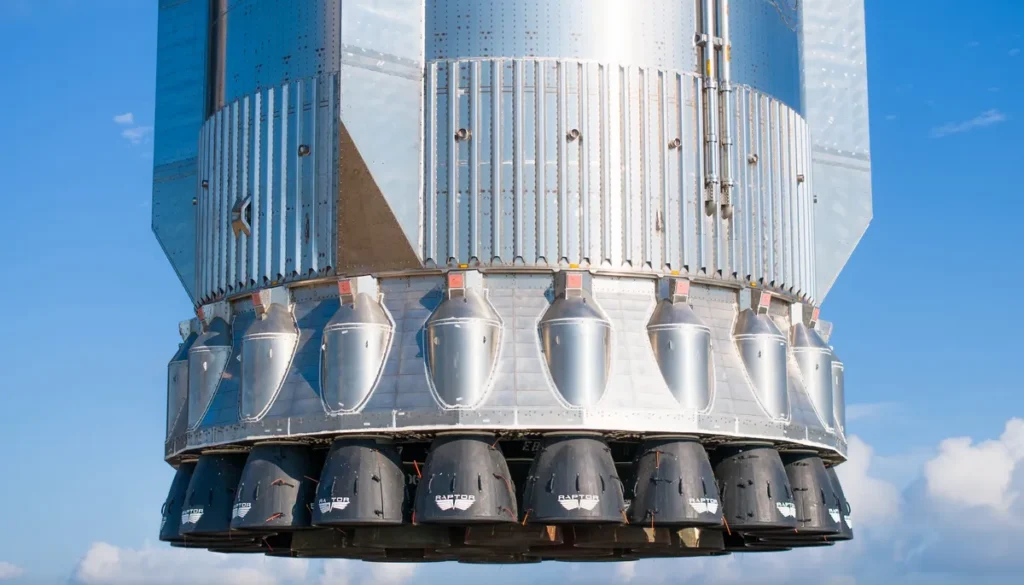

structures, and improved Raptor engine plumbing. Engineers are aiming for longer flight duration, better stability during ascent, and stronger re-entry performance. What makes these upgrades special is how quickly they’re developed. Instead of waiting years for design cycles, SpaceX tests, fails, learns, and rebuilds within months. That’s why Flight 10 has been eagerly
anticipated—it’s not just another launch, it’s a compilation of years of progress packed into one mission. For example, Flight 9 struggled with engine cutoff timing, and those fixes are now embedded into Flight 10. With stronger thrust-to-weight ratio and better thermal
also read SpaceX Starship 10th Test Flight Set After Explosive Setbacks
protection, this vehicle could stay airborne longer and attempt deeper recovery operations. These improvements also push Starship closer to real-
world missions like lunar cargo delivery and, eventually, human spaceflight. By looking at this rollout, you’re not just seeing a rocket—you’re seeing a future spacecraft that might one day land astronauts on Mars.
What Happens Next on the Launch Pad
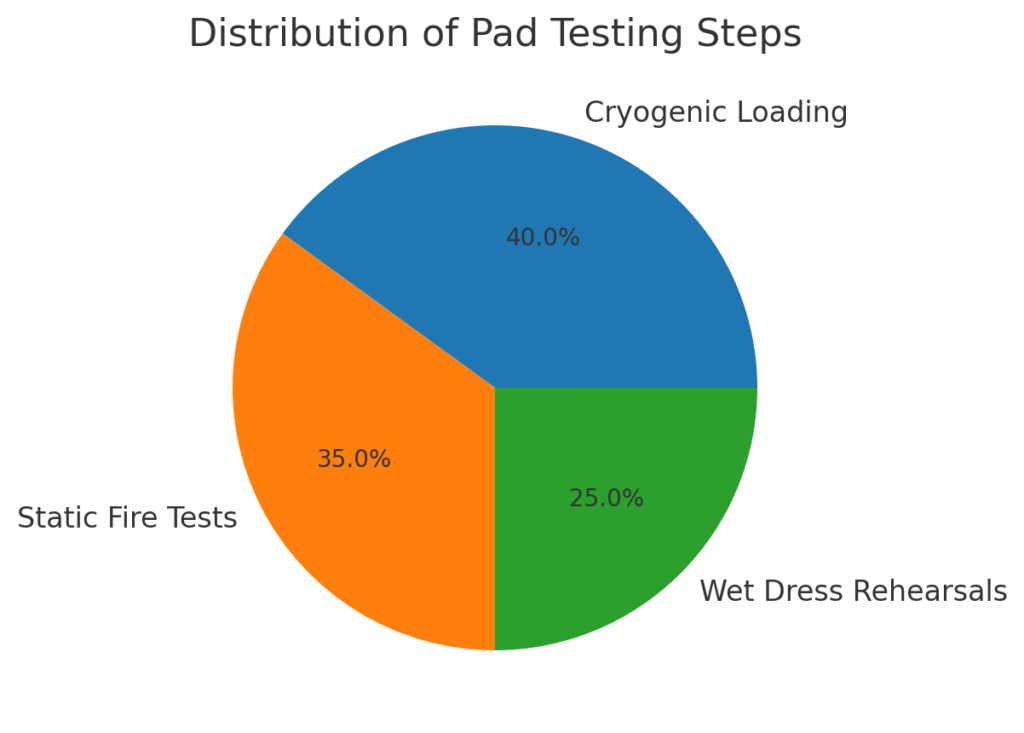
Rolling the super heavy booster out is only the start. The real action happens once the rocket sits on the pad. SpaceX’s team begins connecting massive propellant tanks that will fuel the Raptor engines. These tests include cryogenic fueling trials, where super-cold methane
and oxygen are pumped into the booster. Once that works, they run “static fire” tests—brief firings of all engines while the rocket is clamped down. These are crucial because they simulate launch conditions without leaving the ground. Engineers also check
avionics systems, communication links, and emergency abort sequences. What makes Flight 10 special is that the pad team is racing against both technical and regulatory timelines. Each test is carefully monitored by the Federal Aviation Administration, ensuring every safety box is ticked. Once these are cleared, the booster will be stacked with the Starship upper stage, creating
the full 400-foot-tall rocket. Then comes the final rehearsals: dress rehearsals with countdowns, fueling, and hold procedures. By the time the real countdown begins, both the rocket and its crew o
f engineers will have practiced dozens of times. That’s how Flight 10 will transform from a rollout to a liftoff.
How This Sets the Stage for Lunar and Mars Missions
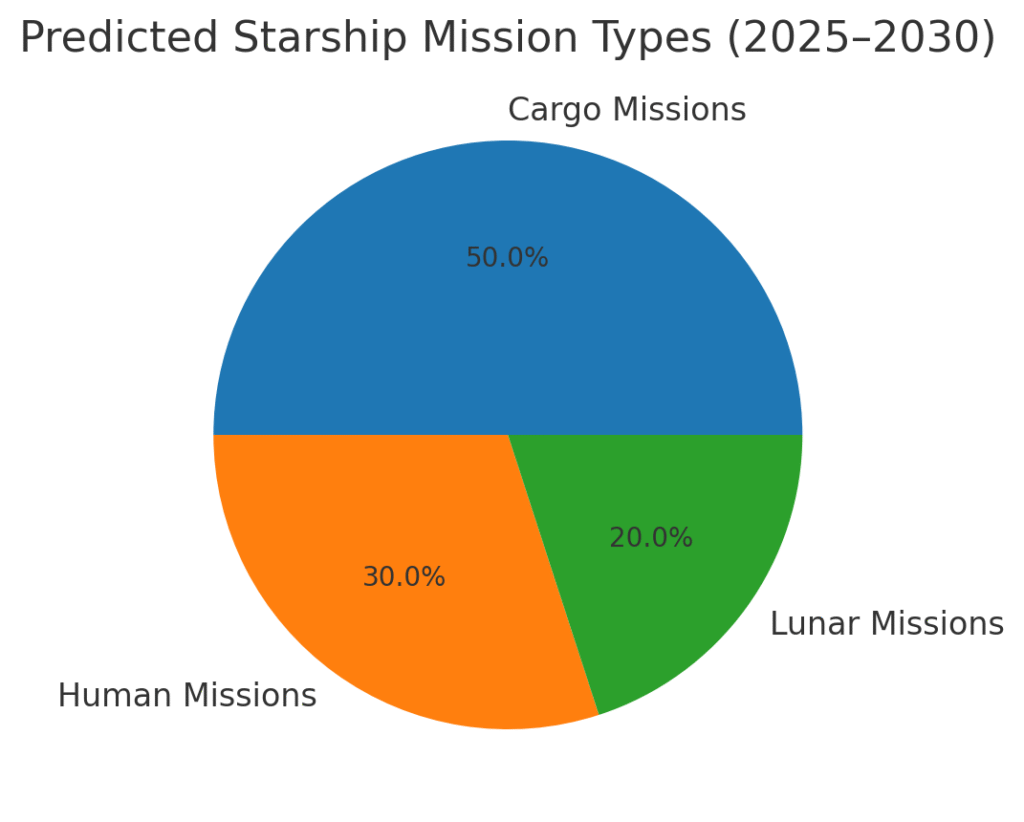
Flight 10 isn’t just about reaching orbit—it’s about preparing for the future. Every time SpaceX rolls a super heavy booster to the pad, they are one step closer to proving Starship’s ability to carry humans and cargo beyond Earth. NASA’s Artemis program is counting on Starship
to land astronauts on the Moon in the coming years. Beyond that, Mars colonization is the ultimate target. Flight 10 is important because it shows whether the system can be scaled, repeated, and trusted for bigger missions. SpaceX also plans to use Starship for launching
massive satellite constellations, interplanetary probes, and even space-based factories. Imagine a rocket powerful enough to send 100 tons to orbit at once—that’s what’s rolling to the pad right now. If Flight 10 succeeds, it will give regulators, investors, and the public
confidence that this system is not just a dream. It’s a working reality. By learning from each step, SpaceX is slowly but surely proving that humanity’s next giant leap will ride on the back of a stainless-steel spacecraft called Starship.
